nginx location的管理以及查找
關于nginx代碼解析,我師兄雕梁的博客(http://simohayha.javaeye.com)有一系列的文章可以閱讀。我這里將只介紹他博客里沒有關注到的或者講述不詳細的,但是我個人又認為是nginx里面比較重要的東西。在這一篇文章里,我將介紹nginx關于location的處理,大家都知道Nginx配置文件里面會有很多的location,nginx的配置指令的作用域可以分為 main,server,location這3個種,實際上這3者不是依次包含的關系,而是相互獨立的關系,比如一個只具有main級別作用域的指令,是不能寫在某個server或者location內的,模塊的某個指令可以同時具有main,server,location這3種作用域,另外每個模塊有 main,srv,loc這3個級別的配置,一個模塊的main級別的配置對所有的server和location都是共享的,srv級別的配置對所有 location都是共享的,location只有自己獨立的loc級別的配置,這就是為什么一個模塊的srv和loc級別的配置需要merge,而 main級別的配置不需要merge的原因。這里看起來有點繞,區分一下main,server,location分別作為一種作用域級別和一個主體,類似于形容詞和名字的區別,nginx的配置關系還是不難理解的。
一般來說一個請求url過來,nginx會將它解析到某一個location來處理。這個解析的過程實際上根據location的配置基本可以分為字符串匹配和正則表達式匹配這2種。對于location的組織方式,最簡單的就是直接將它們保存為一個鏈表,解析url的時候一個一個遍歷即可找到相應location,但是這樣效率太低,對像nginx這種高性能的服務器來說是完全不可取的,nginx將字符串匹配的location組織成了一個三叉的字符串排序樹,而且建立的時候也考慮了樹的平衡性。文章后面我講詳細介紹源碼的實現。
首先我來大概的介紹一下location的種類和匹配規則,以nginx wiki(http://wiki.nginx.org/HttpCoreModule)的例子做說明:
[cpp] view plaincopy
- location = / {
- # matches the query / only.
- [ configuration A ]
- }
- location / {
- # matches any query, since all queries begin with /, but regular
- # expressions and any longer conventional blocks will be
- # matched first.
- [ configuration B ]
- }
- location ^~ /images/ {
- # matches any query beginning with /images/ and halts searching,
- # so regular expressions will not be checked.
- [ configuration C ]
- }
- location ~* \.(gif|jpg|jpeg)$ {
- # matches any request ending in gif, jpg, or jpeg. However, all
- # requests to the /images/ directory will be handled by
- # Configuration C.
- [ configuration D ]
- }
- location @named {
- # Such locations are not used during normal processing of requests,
- # they are intended only to process internally redirected requests (for example error_page, try_files).
- [ configuration E ]
- }
可以看到上面的例子中有5種不同類型的location,其中第4個帶 “~” 號前綴的為需要正則匹配的location,nginx在進行url解析時對這5種不同類型的location具有不同的優先級規則,大致的規則如下:
1,字符串精確匹配到一個帶 “=” 號前綴的location,則停止,且使用這個location的配置;
2,字符串匹配剩下的非正則和非特殊location,如果匹配到某個帶 "^~" 前綴的location,則停止;
3,正則匹配,匹配順序為location在配置文件中出現的順序。如果匹配到某個正則location,則停止,并使用這個location的配置;否則,使用步驟2中得到的具有最大字符串匹配的location配置。
例如,對下面的請求有:
1, / -> 精確匹配到第1個location,匹配停止,使用configuration A
2,/some/other/url -> 首先前綴部分字符串匹配到了第2個location,然后進行正則匹配,顯然沒有匹配上,則使用第2個location的配置configurationB
3,/images /1.jpg -> 首先前綴部分字符串匹配到了第2個location,但是接著對第3個location也前綴匹配上了,而且這時已經是配置文件里面對這個url的最大字符串匹配了,并且location帶有 "^~" 前綴,則不再進行正則匹配,最終使用configuration C
4,/some/other/path/to/1.jpg -> 首先前綴部分同樣字符串匹配到了第2個location,然后進行正則匹配,這時正則匹配成功,則使用congifuration D
nginx的url匹配規則實際上有點不妥,大部分情況下一個url必須先進行字符串匹配,然后再做正則匹配,但是實際上如果先做正則匹配,沒有匹配上再 做字符串匹配,在很多情況下可以節省掉做字符串匹配的時間。不管怎樣,先來看一下nginx源碼里面的實現,在介紹匹配location過程之前,先來介 紹一下nginx里面對location的組織方式,實際上在配置解析階段,nginx將字符串匹配的location和正則匹配的location分別 存儲在http core模塊的loc配置ngx_http_core_loc_conf_t結構的下面2個字段:
[cpp] view plaincopy- ngx_http_location_tree_node_t *static_locations;
- (NGX_PCRE)
- ngx_http_core_loc_conf_t **regex_locations;
- if
從這2個字段的類型可以看出,字符串匹配的location被組織成了一個location tree,而正則匹配的location只是一個數組,location tree和regex_locations數組建立過程在ngx_http_block中:
[cpp] view plaincopy- /* create location trees */
- for (s = 0; s < cmcf->servers.nelts; s++) {
- clcf = cscfp[s]->ctx->loc_conf[ngx_http_core_module.ctx_index];
- if (ngx_http_init_locations(cf, cscfp[s], clcf) != NGX_OK) {
- return NGX_CONF_ERROR;
- }
- if (ngx_http_init_static_location_trees(cf, clcf) != NGX_OK) {
- return NGX_CONF_ERROR;
- }
- }
經過配置的讀取之后,所有server都被保存在http core模塊的main配置中的servers數組中,而每個server里面的location都被按配置中出現的順序保存在http core模塊的loc配置的locations隊列中,上面的代碼中先對每個server的location進行排序和分類處理,這一步發生在 ngx_http_init_location()函數中:
[cpp] view plaincopy- static ngx_int_t
- ngx_http_init_locations(ngx_conf_t *cf, ngx_http_core_srv_conf_t *cscf,
- ngx_http_core_loc_conf_t *pclcf)
- {
- ...
- locations = pclcf->locations;
- ...
- /* 按照類型排序location,排序完后的隊列: (exact_match 或 inclusive) (排序好的,如果某個exact_match名字和inclusive location相同,exact_match排在前面)
- | regex(未排序)| named(排序好的) | noname(未排序)*/
- ngx_queue_sort(locations, ngx_http_cmp_locations);
- named = NULL;
- n = 0;
- #if (NGX_PCRE)
- regex = NULL;
- r = 0;
- #endif
- for (q = ngx_queue_head(locations);
- q != ngx_queue_sentinel(locations);
- q = ngx_queue_next(q))
- {
- lq = (ngx_http_location_queue_t *) q;
- clcf = lq->exact ? lq->exact : lq->inclusive;
- /* 由于可能存在nested location,也就是location里面嵌套的location,這里需要遞歸的處理一下當前location下面的nested location */
- if (ngx_http_init_locations(cf, NULL, clcf) != NGX_OK) {
- return NGX_ERROR;
- }
- #if (NGX_PCRE)
- if (clcf->regex) {
- r++;
- if (regex == NULL) {
- regex = q;
- }
- continue;
- }
- #endif
- if (clcf->named) {
- n++;
- if (named == NULL) {
- named = q;
- }
- continue;
- }
- if (clcf->noname) {
- break;
- }
- }
- if (q != ngx_queue_sentinel(locations)) {
- ngx_queue_split(locations, q, &tail);
- }
- /* 如果有named location,將它們保存在所屬server的named_locations數組中 */
- if (named) {
- clcfp = ngx_palloc(cf->pool,
- (n + 1) * sizeof(ngx_http_core_loc_conf_t **));
- if (clcfp == NULL) {
- return NGX_ERROR;
- }
- cscf->named_locations = clcfp;
- for (q = named;
- q != ngx_queue_sentinel(locations);
- q = ngx_queue_next(q))
- {
- lq = (ngx_http_location_queue_t *) q;
- *(clcfp++) = lq->exact;
- }
- *clcfp = NULL;
- ngx_queue_split(locations, named, &tail);
- }
- #if (NGX_PCRE)
- /* 如果有正則匹配location,將它們保存在所屬server的http core模塊的loc配置的regex_locations 數組中,
- 這里和named location保存位置不同的原因是由于named location只能存在server里面,而regex location可以作為nested location */
- if (regex) {
- clcfp = ngx_palloc(cf->pool,
- (r + 1) * sizeof(ngx_http_core_loc_conf_t **));
- if (clcfp == NULL) {
- return NGX_ERROR;
- }
- pclcf->regex_locations = clcfp;
- for (q = regex;
- q != ngx_queue_sentinel(locations);
- q = ngx_queue_next(q))
- {
- lq = (ngx_http_location_queue_t *) q;
- *(clcfp++) = lq->exact;
- }
- *clcfp = NULL;
- ngx_queue_split(locations, regex, &tail);
- }
- #endif
- return NGX_OK;
- }
上面的步驟將正則匹配的location保存好了,location tree的建立在ngx_http_init_static_location_trees中進行:
[cpp] view plaincopy- static ngx_int_t
- ngx_http_init_static_location_trees(ngx_conf_t *cf,
- ngx_http_core_loc_conf_t *pclcf)
- {
- ngx_queue_t *q, *locations;
- ngx_http_core_loc_conf_t *clcf;
- ngx_http_location_queue_t *lq;
- locations = pclcf->locations;
- if (locations == NULL) {
- return NGX_OK;
- }
- if (ngx_queue_empty(locations)) {
- return NGX_OK;
- }
- /* 這里也是由于nested location,需要遞歸一下 */
- for (q = ngx_queue_head(locations);
- q != ngx_queue_sentinel(locations);
- q = ngx_queue_next(q))
- {
- lq = (ngx_http_location_queue_t *) q;
- clcf = lq->exact ? lq->exact : lq->inclusive;
- if (ngx_http_init_static_location_trees(cf, clcf) != NGX_OK) {
- return NGX_ERROR;
- }
- }
- /* join隊列中名字相同的inclusive和exact類型location,也就是如果某個exact_match的location名字和普通字符串匹配的location名字相同的話,
- 就將它們合到一個節點中,分別保存在節點的exact和inclusive下,這一步的目的實際是去重,為后面的建立排序樹做準備 */
- if (ngx_http_join_exact_locations(cf, locations) != NGX_OK) {
- return NGX_ERROR;
- }
- /* 遞歸每個location節點,得到當前節點的名字為其前綴的location的列表,保存在當前節點的list字段下 */
- ngx_http_create_locations_list(locations, ngx_queue_head(locations));
- /* 遞歸建立location三叉排序樹 */
- pclcf->static_locations = ngx_http_create_locations_tree(cf, locations, 0);
- if (pclcf->static_locations == NULL) {
- return NGX_ERROR;
- }
- return NGX_OK;
- }
經過ngx_http_init_location()函數處理之后,locations隊列已經是排好序的了,建立三叉樹的過程的主要工作都在ngx_http_create_locations_list()和ngx_http_create_locations_tree()中完成,這2個 函數都是遞歸函數,第1個函數遞歸locations隊列中的每個節點,得到以當前節點的名字為前綴的location,并保存在當前節點的list字段 下,例如,對下列location:
[cpp] view plaincopy- location /xyz {
- }
- location = /xyz {
- }
- location /xyza {
- }
- location /xyzab {
- }
- location /xyzb {
- }
- location /abc {
- }
- location /efg {
- }
- location /efgaa {
- }
排序的結果為/abc /efg /efgaa =/xyz /xyz /xyza /xyzab /xyzb,去重后結果為 /abc /efg /efgaa /xyz /xyza /xyzab/xyzb,ngx_http_create_locations_list()執行后的結果為:
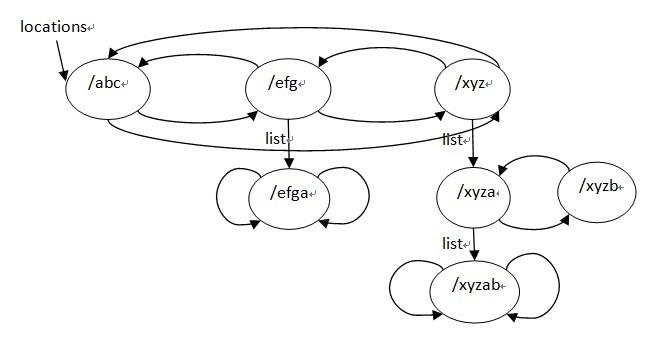
最后,來看下ngx_http_create_locations_tree函數:
[cpp] view plaincopy
- static ngx_http_location_tree_node_t *
- ngx_http_create_locations_tree(ngx_conf_t *cf, ngx_queue_t *locations,
- size_t prefix)
- {
- ...
- /* 根節點為locations隊列的中間節點 */
- q = ngx_queue_middle(locations);
- lq = (ngx_http_location_queue_t *) q;
- len = lq->name->len - prefix;
- node = ngx_palloc(cf->pool,
- offsetof(ngx_http_location_tree_node_t, name) + len);
- if (node == NULL) {
- return NULL;
- }
- node->left = NULL;
- node->right = NULL;
- node->tree = NULL;
- node->exact = lq->exact;
- node->inclusive = lq->inclusive;
- node->auto_redirect = (u_char) ((lq->exact && lq->exact->auto_redirect)
- || (lq->inclusive && lq->inclusive->auto_redirect));
- node->len = (u_char) len;
- ngx_memcpy(node->name, &lq->name->data[prefix], len);
- /* 從中間節點開始斷開 */
- ngx_queue_split(locations, q, &tail);
- if (ngx_queue_empty(locations)) {
- /*
- * ngx_queue_split() insures that if left part is empty,
- * then right one is empty too
- */
- goto inclusive;
- }
- /* 從locations左半部分得到左子樹 */
- node->left = ngx_http_create_locations_tree(cf, locations, prefix);
- if (node->left == NULL) {
- return NULL;
- }
- ngx_queue_remove(q);
- if (ngx_queue_empty(&tail)) {
- goto inclusive;
- }
- /* 從locations右半部分得到右子樹 */
- node->right = ngx_http_create_locations_tree(cf, &tail, prefix);
- if (node->right == NULL) {
- return NULL;
- }
- inclusive:
- if (ngx_queue_empty(&lq->list)) {
- return node;
- }
- /* 從list隊列得到tree子樹 */
- node->tree = ngx_http_create_locations_tree(cf, &lq->list, prefix + len);
- if (node->tree == NULL) {
- return NULL;
- }
- return node;
- }
location tree節點的ngx_http_location_tree_node_s結構:
[cpp] view plaincopy- struct ngx_http_location_tree_node_s {
- ngx_http_location_tree_node_t *left;
- ngx_http_location_tree_node_t *right;
- ngx_http_location_tree_node_t *tree;
- ngx_http_core_loc_conf_t *exact;
- ngx_http_core_loc_conf_t *inclusive;
- u_char auto_redirect;
- u_char len;
- u_char name[1];
- };
location tree結構用到的是left,right,tree 這3個字段, location tree實際上是一個三叉的字符串排序樹,而且這里如果某個節點只考慮左,右子樹,它是一顆平衡樹,它的建立過程有點類似于一顆平衡排序二叉樹的建立過程,先排序再用二分查找找到的節點順序插入,ngx_http_location_tree_node_s的tree節點也是一顆平衡排序樹,它是用該節點由ngx_http_create_locations_list()得到的list建立的,也就是該節點的名字是它的tree子樹里面的所有節點名字的前綴,所以tree子樹里面的所有節點的名字不用保存公共前綴,而且查找的時候,如果是轉向tree節點的話,也是不需要再比較父節點的那段字符串了。
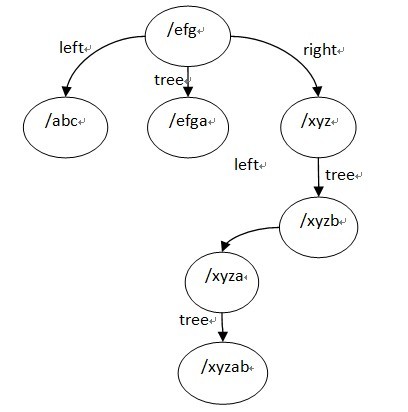
ngx_http_create_locations_tree()函數寫的很清晰,它有一個參數是隊列locations,它返回一顆三叉樹,根節點為locations的中間節點,其左子樹為locations隊列的左半部分建立的location tree,右子樹為location隊列的右半部分建立的tree,tree節點為該根節點的list隊列建立的tree。
最終建立的location tree如下(為了方便閱讀,圖中列出了tree節點的完整名字):
location的匹配發生在nginx請求處理的NGX_HTTP_FIND_CONFIG_PHASE階段(請求的處理所有PHASE可以看這篇博客http://simohayha.iteye.com/blog/670326),匹配的規則文章前面已經做過介紹,源碼的實現也很簡單,這里不再做介紹了。
from:http://blog.csdn.net/fengmo_q/article/details/6683377
RFID管理系統集成商 RFID中間件 條碼系統中間層 物聯網軟件集成


